Solution:
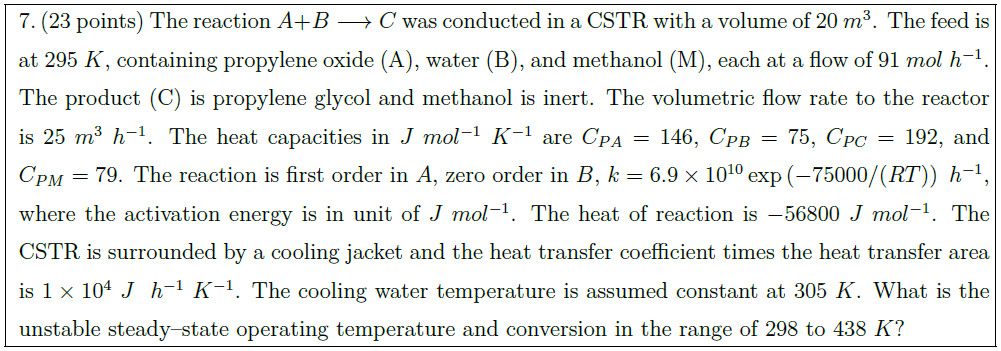
The reaction $A + B \longrightarrow C$ was conducted in a CSTR with a volume of $20\ m^3$. The feed is at $295\ K$, containing propylene oxide (A), water (B), and methanol (M), each at a flow of $91\ mol\ h^{-1}$. The product (C) is propylene glycol and methanol is inert. The volumetric flow rate to the reactor is $25\ m^3\ h^{-1}$. The heat capacities in $J\ mol^{-1}\ K^{-1}$ are $C_{PA} = 146$, $C_{PB} = 75$, $C_{PC} = 192$, and $C_{PM} = 79$.
The reaction is first order in $A$, zero order in $B$, $k = 6.9 \times 10^{10} \exp \left( -75000/(RT) \right)\ h^{-1}$, where the activation energy is in unit of $J\ mol^{-1}$. The heat of reaction is $-56800\ J\ mol^{-1}$. The CSTR is surrounded by a cooling jacket and the heat transfer coefficient times the heat transfer area is $1 \times 10^4\ J\ \ h^{-1}\ K^{-1}$. The cooling water temperature is assumed constant at $305\ K$. What is the unstable steady–state operating temperature and conversion in the range of $298$ to $438\ K$?