Solution:
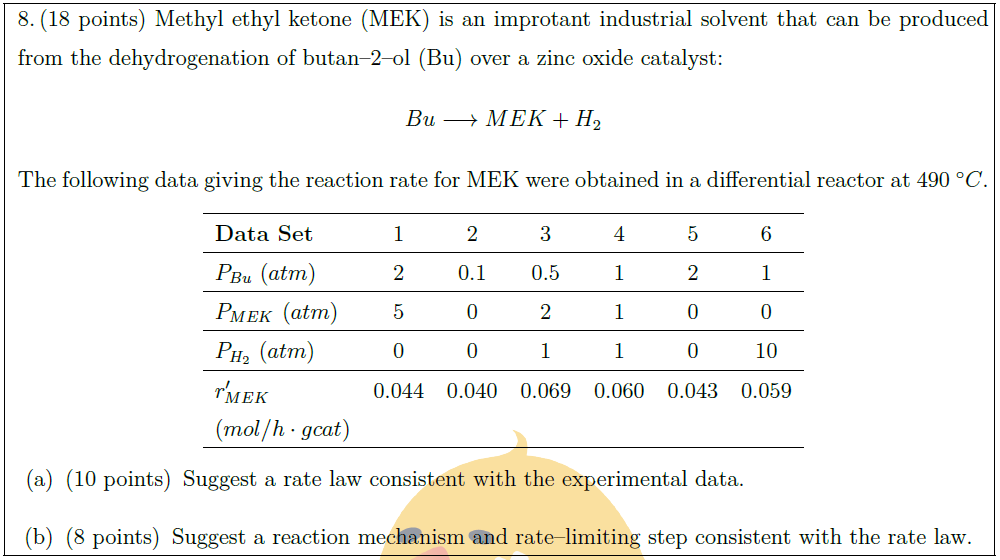
Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) is an improtant industrial solvent that can be produced from the dehydrogenation of butan–2–ol (Bu) over a zinc oxide catalyst:
\begin{align*}
Bu \longrightarrow MEK + H_2
\end{align*}
The following data giving the reaction rate for MEK were obtained in a differential reactor at $490\ ^\circ C$.
\begin{center}
\begin{tabular}{lcccccc}
\hline
{\bf Data Set} & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 6\\
\hline
$P_{Bu}\ (atm)$ & 2 & 0.1 & 0.5 & 1 & 2 & 1\\
\hline
$P_{MEK}\ (atm)$ & 5 & 0 & 2 & 1 & 0 & 0\\
\hline
$P_{H_2}\ (atm)$ & 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 10\\
\hline
$r’_{MEK}$ & 0.044 & 0.040 & 0.069 & 0.060 & 0.043 & 0.059\\
$(mol / h \cdot gcat)$ & & & & & &\\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{center}
\begin{parts}
\part [10] Suggest a rate law consistent with the experimental data.
\part [8] Suggest a reaction mechanism and rate–limiting step consistent with the rate law.
\end{parts}